A monostable multivibrator (MMV) often called a one-shot multivibrator, is a pulse generator circuit in which the duration of the pulse is determined by the R-C network,connected externally to the 555 timer. In such a vibrator, one state of output is stable while the other is quasi-stable (unstable). For auto-triggering of output from quasi-stable state to stable state energy is stored by an externally connected capacitor C to a reference level. The time taken in storage determines the pulse width. The transition of output from stable state to quasi-stable state is accomplished by external triggering. The schematic of a 555 timer in monostable mode of operation is shown in figure.
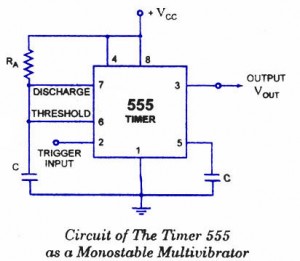
Monostable Multivibrator Circuit details
Pin 1 is grounded. Trigger input is applied to pin 2. In quiescent condition of output this input is kept at + VCC. To obtain transition of output from stable state to quasi-stable state, a negative-going pulse of narrow width (a width smaller than expected pulse width of output waveform) and amplitude of greater than + 2/3 VCC is applied to pin 2. Output is taken from pin 3. Pin 4 is usually connected to + VCC to avoid accidental reset. Pin 5 is grounded through a 0.01 u F capacitor to avoid noise problem. Pin 6 (threshold) is shorted to pin 7. A resistor RA is connected between pins 6 and 8. At pins 7 a discharge capacitor is connected while pin 8 is connected to supply VCC.
555 IC Monostable Multivibrator Operation.
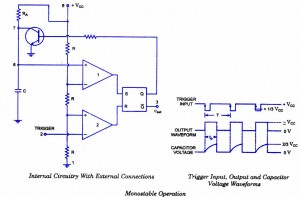
For explaining the operation of timer 555 as a monostable multivibrator, necessary internal circuitry with external connections are shown in figure.
The operation of the circuit is explained below:
Initially, when the output at pin 3 is low i.e. the circuit is in a stable state, the transistor is on and capacitor- C is shorted to ground. When a negative pulse is applied to pin 2, the trigger input falls below +1/3 VCC, the output of comparator goes high which resets the flip-flop and consequently the transistor turns off and the output at pin 3 goes high. This is the transition of the output from stable to quasi-stable state, as shown in figure. As the discharge transistor is cutoff, the capacitor C begins charging toward +VCC through resistance RA with a time constant equal to RAC. When the increasing capacitor voltage becomes slightly greater than +2/3 VCC, the output of comparator 1 goes high, which sets the flip-flop. The transistor goes to saturation, thereby discharging the capacitor C and the output of the timer goes low, as illustrated in figure.
Thus the output returns back to stable state from quasi-stable state.
The output of the Monostable Multivibrator remains low until a trigger pulse is again applied. Then the cycle repeats. Trigger input, output voltage and capacitor voltage waveforms are shown in figure.
Monostable Multivibrator Design Using 555 timer IC
The capacitor C has to charge through resistance RA. The larger the time constant RAC, the longer it takes for the capacitor voltage to reach +2/3VCC.
In other words, the RC time constant controls the width of the output pulse. The time during which the timer output remains high is given as
tp = 1.0986 RAC
where RA is in ohms and C is in farads. The above relation is derived as below. Voltage across the capacitor at any instant during charging period is given as
vc = VCC (1- e-t/RAC)
Substituting vc = 2/3 VCC in above equation we get the time taken by the capacitor to charge from 0 to +2/3VCC.
So +2/3VCC. = VCC. (1 – e-t/RAC) or t – RAC loge 3 = 1.0986 RAC
So pulse width, tP = 1.0986 RAC s 1.1 RAC
The pulse width of the circuit may range from micro-seconds to many seconds. This circuit is widely used in industry for many different timing applications.
Share this on your favourite network







Gud explanation and it is useful to us.
ReplyDeleteFor ece important points & formulas CLICK HERE