The diac and the silicon bilateral switch are grouped as bilateral or bidirectional devices because they can breakover in either direction. There are also breakover devices which breakover in only one direction; they fall in the category of unilateral or unidirectional breakover devices. Although unilateral breakover devices are more frequently employed in SCR triggering, they can also be employed in triac triggering circuit if they have some extra supporting circuitry. Silicon unilateral switch (SUS) is one of the important unilateral breakover devices.
V-I characteristic of SUS
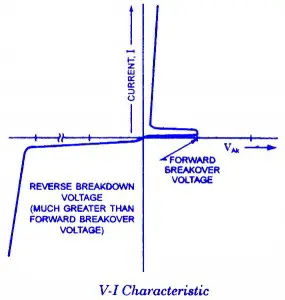
The schematic symbol and V-I characteristic of SUS are shown is figure a and b respectively. The SUS, like the SBS, has gate terminal which can change the basic breakover characteristic shown in figure. By connecting a Zener diode between the gate and the cathode of an SUS, the breakover voltage can be reduced to (VZ + 0.6 V).This is accomplished by connecting Zener diode cathode to the SUS gate and Zener diode anode to the SUS cathode. SUS can be fired at a very low anode to cathode’ voltage (approximately 1 V) if gate current flows from anode to gate. SUSs are low-voltage, low-current devices. Most SUSs have a breakover voltage of 8 V and a current limit of less than 1 A.
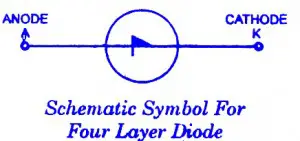
Four-layer diode
Four-layer diode is another unilateral breakover device. Its schematic symbol is shown in figure. The V-I characteristic for four-layer diode-.and SUS are the same and are illustrated in figure. The V-I characteristic of four-layer diodes and SUSs is similar to that of an SBS except that only forward breakover voltage is possible. Reverse break-down can happen, but only at a much greater voltage level than + VB0. Reverse breakdown is destructive for the device. The breakover behaviour of a four layer diode cannot be changed. Four layer diodes are available with breakover voltages ranging from 10 to 400 V. They can carry large pulsed currents if the pulses are of short duration. Some four-layer diodes can carry 100 A current pulses.
Share this on your favourite network







0 comments:
Post a Comment